An IPSEC IKE flood is a layer 5 DDoS attack that tries to consume a targeted victim VPN server resources in order to bring a DoS state to a VPN service.
This DDoS attack is normally done by sending rapid IPSEC IKE requests to a VPN server within the network via port 500, possibly with a spoofed source IP, making the VPN server respond back with IKE traffic. The resource consumption takes place on the victim VPN server.
Technical Analysis
Below is an analysis of an IPSEC IKE flood running from a single SRC attacking IP at a high rate to a single destination target IP.
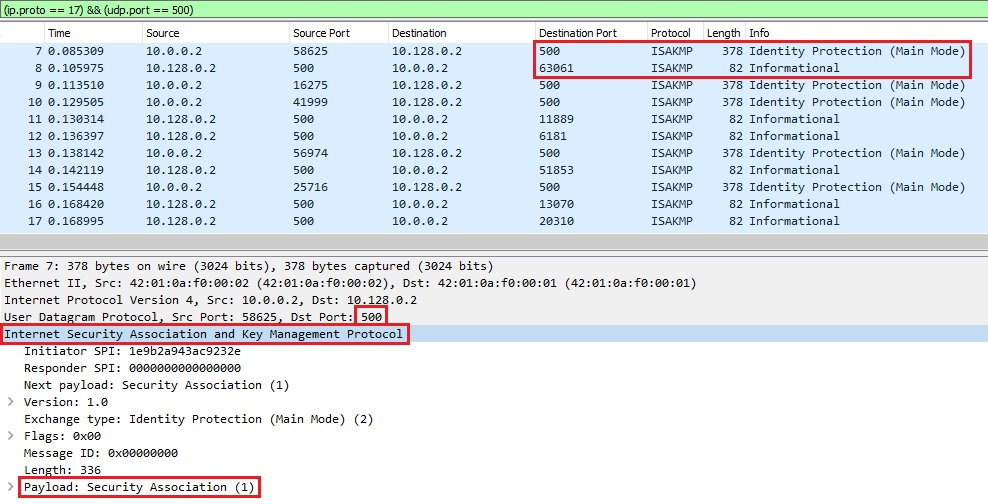
In Image 1 below we can see multiple IKE requests being sent to a victim VPN server. we can see the destination port set to 500 and the protocol used is ISAKMP.
“Image 1 – Example of single IPSEC IKEv1 Flood packet being sent to port 500”
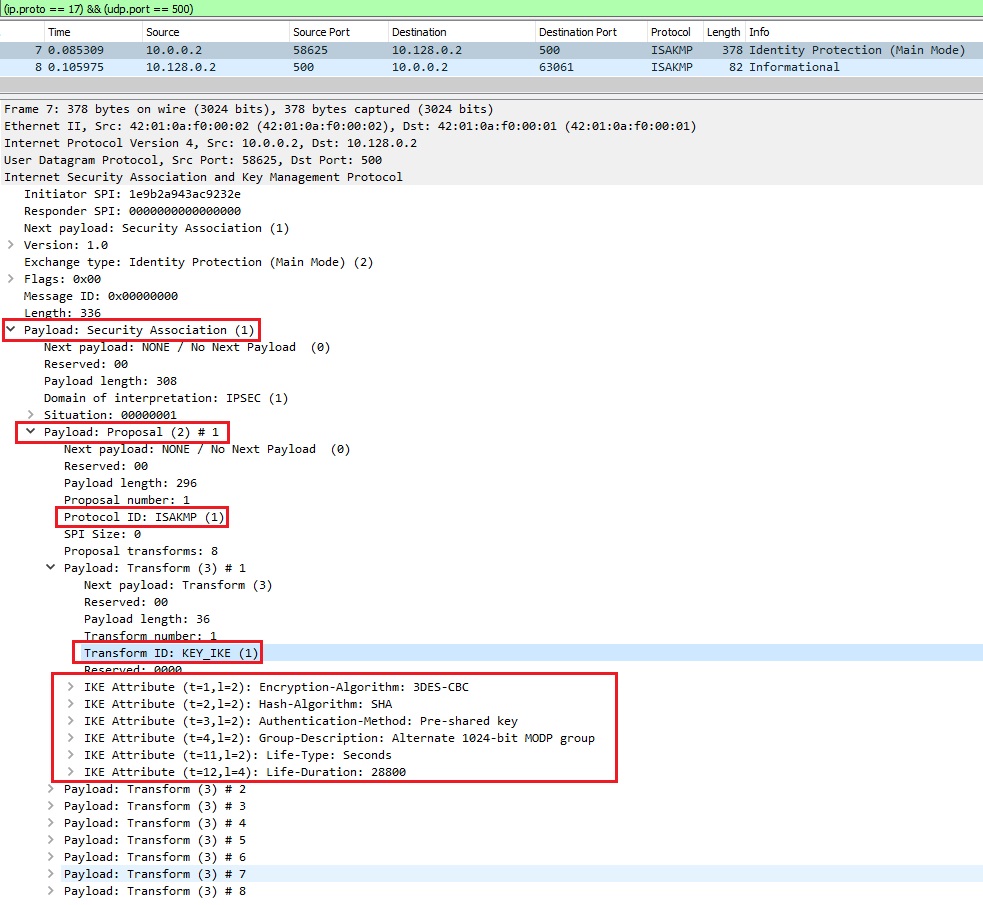
As seen in Image 2, looking at the ISAKMP payload – we see IKE requests being sent as a legitimate offer to the victim VPN server.
“Image 2 – ISAKMP Payload”
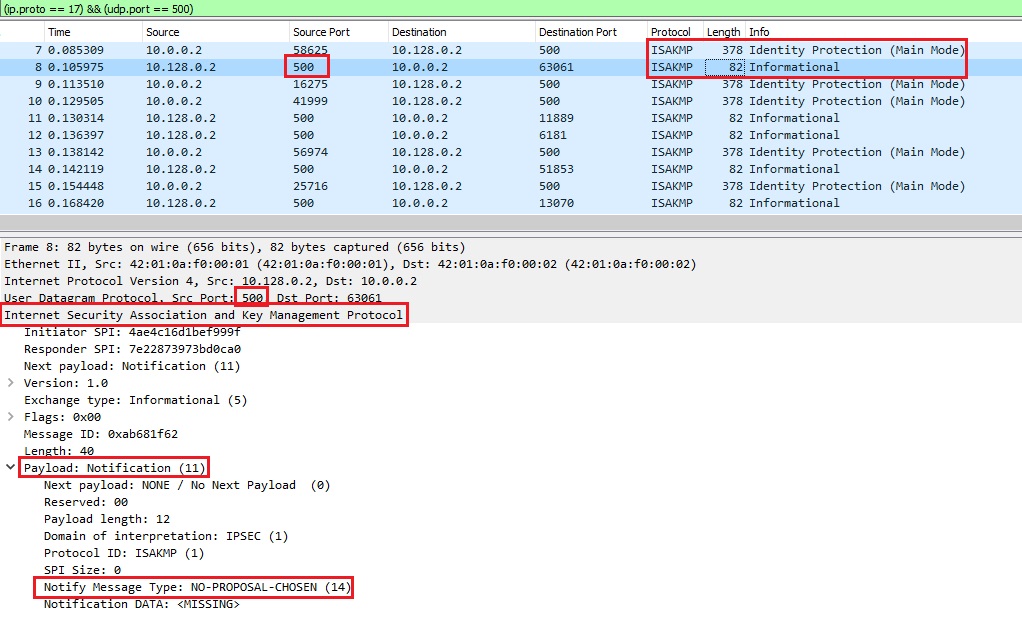
In Image 3 below we see the victim VPN server responds back to our IKE requests. We can see the notify message in the ISAKMP payload: “NO-PROPOSAL-CHOSEN” – in this scenario – which indicates there is a mismatch of proposals during phase 1 or phase 2 negotiation.
“Image 3 – VPN server response back”
The rate of this flood is shown in Image 4, at around 70 PPS (Packets Per Second) with an average packet size of 230 bytes. A high PPS value per source IP is a strong indication that an attack is taking place.
“Image 4 – IPSEC IKE Flood rate from single SRC IP to Single Target DST IP”

IPSEC IKE Flood is a resource consumption flood due to the actions executed on the victim VPN server following the IKE requests. The identification of this type of flood is possible by counting the number of PPS towards the victim VPN server and by looking at the ISAKMP payload information.
Analysis of an IPSEC IKE flood in Wireshark – Filters
Filter out UDP packets going to port 500 – “(ip.proto == 17) && (udp.port == 500)”
Or filter out only the ISAKMP protocol – “isakmp”
Go to Statistics -> Summary on the menu bar to understand the rate you are looking at.
Download Example PCAP of IPSEC IKE Flood
*Note: IP’s have been randomized to ensure privacy.
Download