HTTP GET flood is a layer 7 DDoS attack that targets web servers and applications.
Layer 7 is the application layer of the OSI model. The HTTP protocol – is an Internet protocol which is the basis of browser-based Internet requests, and is commonly used to send form contents over the Internet or to load web pages.
HTTP GET floods are designed to overwhelm web servers’ resources by continuously requesting single or multiple URL’s from many source attacking machines, which simulate a HTTP clients, such as web browsers (Though the attack analyzed here, does not use browser emulation).
An HTTP GET Flood consist of GET requests. Unlike other HTTP floods that may include other request methods such as POST, PUT, DELETE etc.
When the server’s limits of concurrent connections are reached, the server can no longer respond to legitimate requests from other clients attempting to connect, causing a denial of service.
HTTP GET flood attacks use standard URL requests, hence it may be quite challenging to differentiate from valid traffic. Traditional rate-based volumetric detection, is ineffective in detecting HTTP GET flood attacks, since traffic volume in HTTP GET floods is often under detection thresholds.
Technical analysis
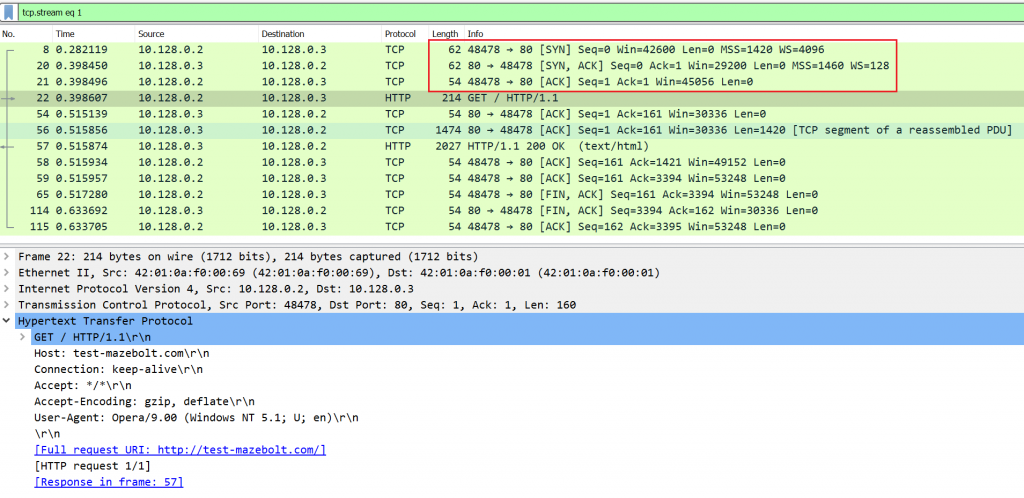
To send HTTP GET request client establishes TCP connection. Before sending a HTTP GET request a TCP connection between a client and a server is established, using 3-Way Handshake (SYN, SYN-ACK, ACK) , seen in packets 8,20,21 in Image 1. The HTTP request will be in a PSH, ACK packet.
Image 1 – Example of TCP connection
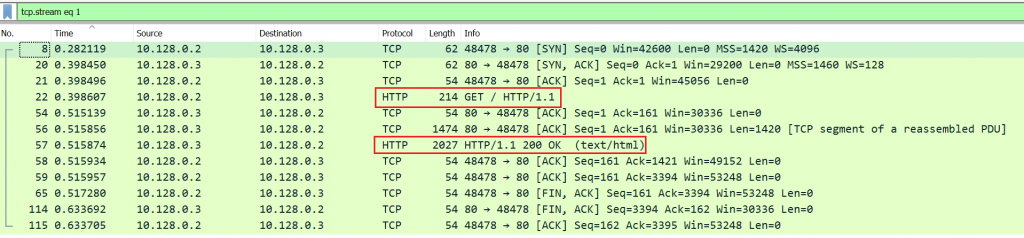
An attacker (IP 10.128.0.2) sends GET / HTTP / 1.1 requests, while the target responds with HTTP/1.1 200 OK as seen in Image 2.
Image 2 – Example of HTTP packets exchange between an attacker and a target:
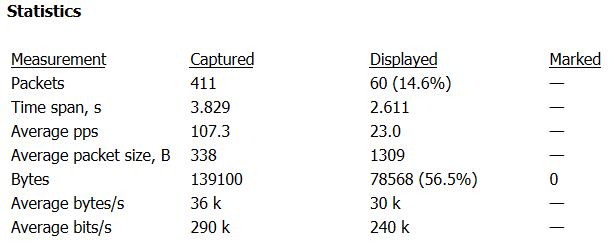
As seen in image 3. The capture analyzed is around 3.8 seconds and the average number of packets per second is around 107 PPS, with a rate of around 0.29 Mbps per second (considered low, the attack you are analyzing could be significantly higher).
Image 3 – HTTP Flood stats
Analysis of HTTP GET Flood in WireShark – Filters
“http” filter – Will show all http related packets.
“http.request.method == GET” – Will show HTTP GET requests.
It will be important to review the user agent and other HTTP header structures as well as the timing of each request to understand the attack underway.
Download example PCAP of HTTP GET Flood attack
*Note: IP’s have been randomized to ensure privacy.
Download