Empty connection floods are DDoS attacks designed to saturate the targeted open port’s sockets. The idea is that as connections increase you are saturating the TCP stack to finally bring about a situation whereby the particular daemon/service is unable to accept any new connections.
An Empty connection flood may also saturate other stateful devices in its path such as firewall’s or IPS systems.
Technical Analysis
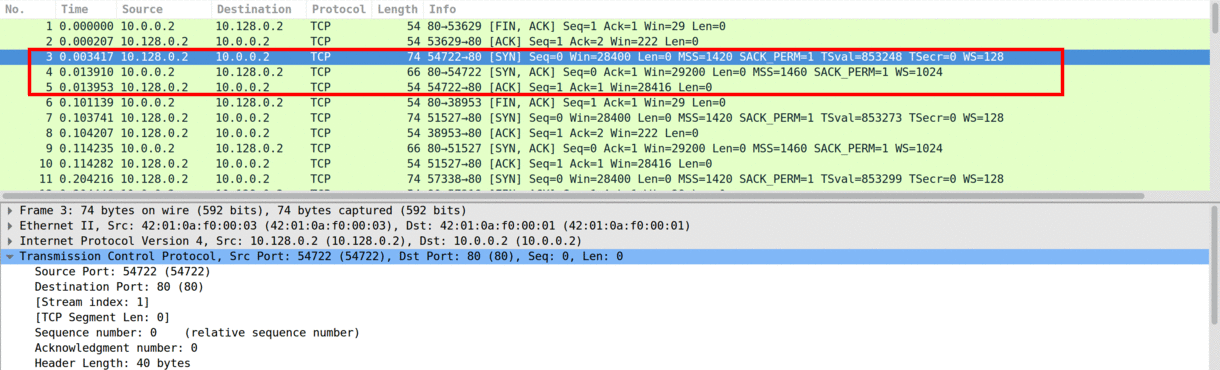
As seen in Image 1, An Empty Connection flood starts and ends with a TCP Handshake. The attacker (here 10.128.0.2) sends a SYN packet. The victim (with IP 10.0.0.2) responds with a SYN-ACK packet, and finally, the attacker sends an ACK packet – establishing the TCP connection.
“Image 1: The TCP Handshake”
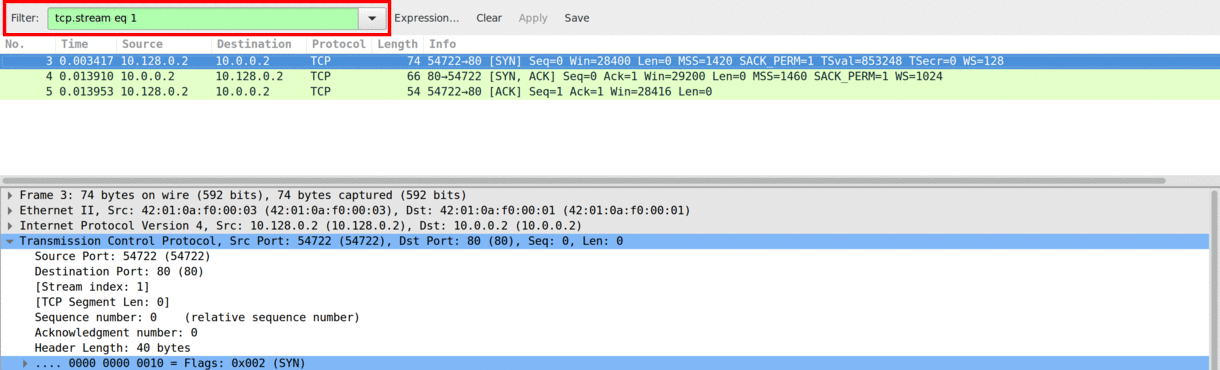
As seen in Image 2, after establishing the connection, the attacker will not send any more data, and proceed to open new TCP connections. Using a filter for a specific TCP stream (Conversation), the connection is empty, meaning no other packets were sent. Sometimes the victim may end the connection after it has timed out with a FIN, FIN-ACK, ACK exchange.
“Image 2: The Connection is Empty!”
Analysis of Empty Connection Flood in Wireshark
Tracking of TCP handshakes can be done by using the “tcp” filter. To find out how many connections were opened between the various machines talking, click on “Statistics” -> “Conversations”.
If you see a single source IP opening many connections, it could be an attacker.