A Memcrashed Random is a reflection-amplification DDoS attack. The attacker spoofs requests to vulnerable UDP memcache servers, which sends a larger reply to the targeted victim, potentially overwhelming the victim’s resources. While the target’s network infrastructure is overloaded, legitimate traffic cannot access the network.
When the targeted server’s network bandwidth gets saturated, other legitimate traffic cannot reach its destination, causing a denial of service.
Memcrashed amplification is one of the highest out of all the amplification attack vectors, with a factor of up to 51,000
Technical Analysis
Below is an analysis of a Memcrashed Random running from a single source attacking IP at a high rate to a single destination target IP.
Because Memcrashed Random is a reflection attack, the source port on the attack datagram is 11211 UDP (Memcache service port), and the destination port is the victim port.
The size of the Memcache response datagram can vary greatly depending on the vulnerable Memcache server used and the requested query, but it tends to be on the larger side; in this case, the server returned a fixed payload size of 1400.
The response traffic usually falls into one of two patterns: Random, in which the server responds with its stored memory, or Stats, in which the server responds with stats about its saved data.
Image 1 – Memcrashed Random – reflection
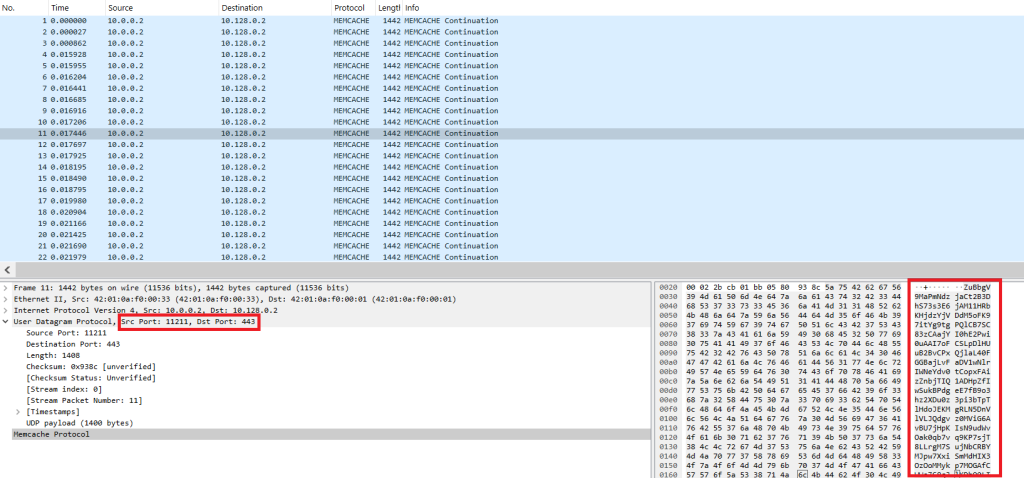
The captured analysis is around 10 seconds long and contains an average of 3900 PPS (packets per second). A real attack will use many sources and at much higher rates.

Analysis of Memcrashed Random in Wireshark – Filters
Memcache uses the UDP protocol, so we can at least use the “udp” filter.
The “memcache” filter will show all memcache packets.
The “udp.srcport==11211” will show all Memcache response traffic.
Memcache traffic is usually requested only by consenting parties, so if you received memcache traffic from a source you don’t expect, it’s likely a Memcrashed attack
Download